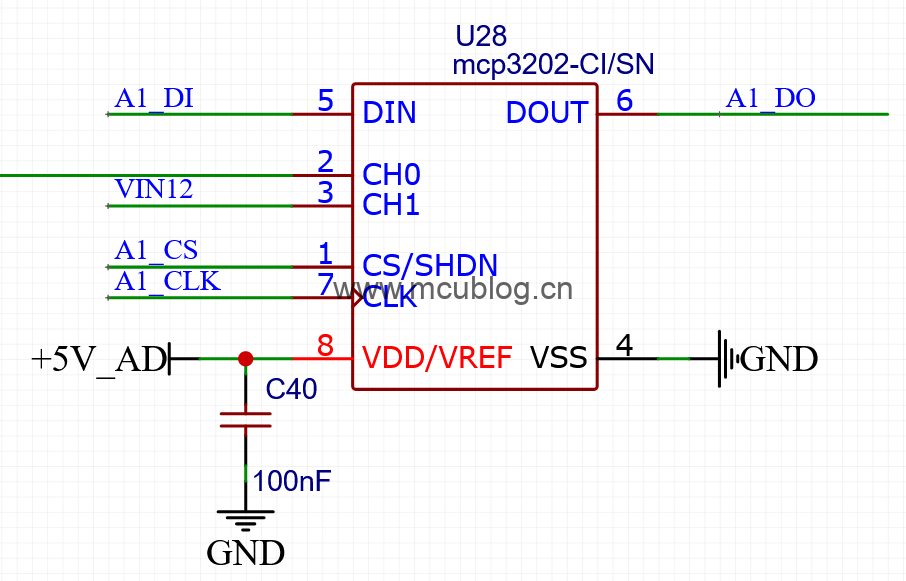
之前介绍过使用STM32的AD采样功能,采集外部电压。这次介绍AD转换芯片MCP3202,是美国MICROCHIP公司推出的一款双通道、12位分辨率的AD采样芯片。外部提供了SPI接口(支持00模式和11模式),可以实现数据的快速读取。芯片原理图如下:
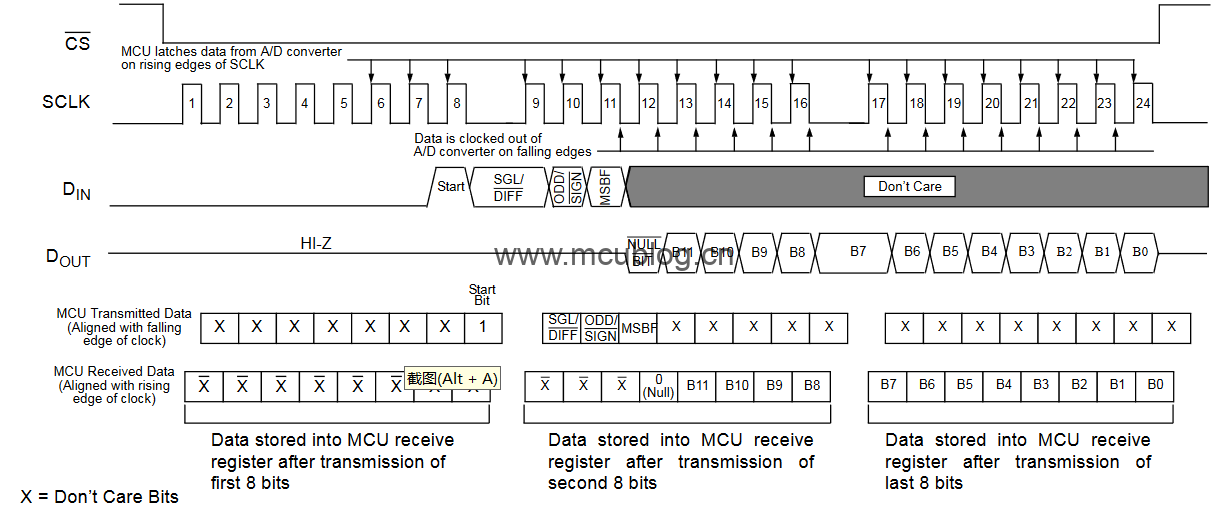
虽然提供了SPI接口,但读取数据时,会发现并不是标准的SPI接口。如果使用的是MCU,参照这个时序图:
如果使用的是FPGA,参照这个时序图:
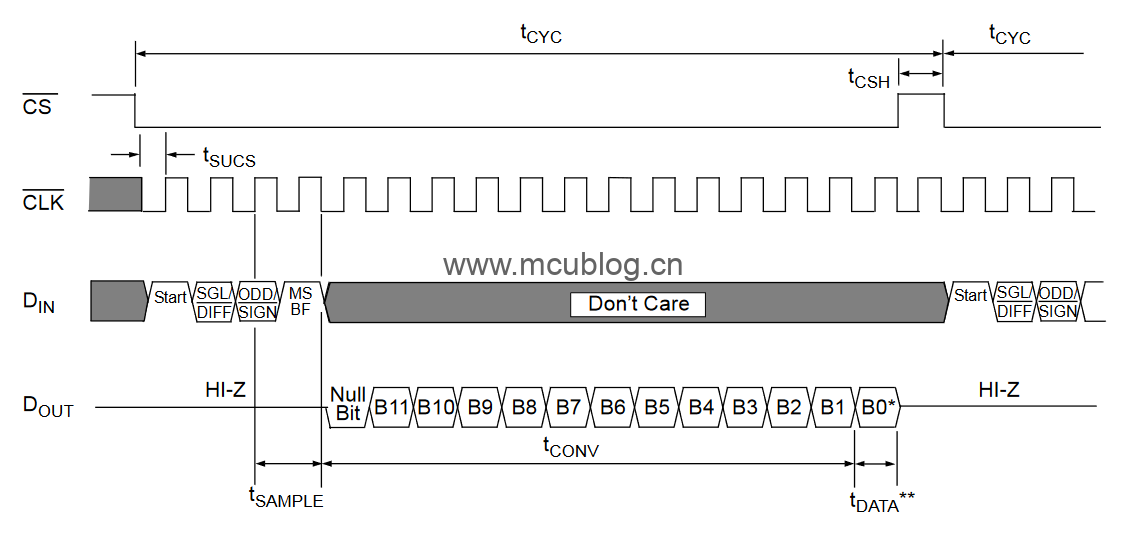
本文只说FPGA方面,所以看第二个图(上图)。从图中可知,当片选(CS)拉低以后,CLK提供了17个时钟,是的,不是8个,不是16个,是17个,这就是为什么说它不是标准的SPI接口。
拉低后,第一个时钟内,DIN提供高电平,告诉芯片开始转换;
第二、第三个时钟,配置高低电平,选择相应的通道(通道0、通道1)、模式(单端、差分)。
第四个时钟,配置数据是高位在前(MSB)还是低位在前(LSB)。
第五个时钟,空的,啥都不用管。
后面12个时钟,DIN上面的电平就无所谓了,只看DOUT上面的电平,它代表AD采样的数据。
搞明白它的工作方式,就可以开始写代码了。
首先写一段代码,提供18个时钟,及相应的CS信号。
为什么是18个?不是17个吗?
因为每次转换完成之后,CS要拉高持续一段时间,这个时间刚好可以用一个CLK来抵消。因此时钟及CS在这里完成。
--串行数据所需时钟的各个状态
type SclkState is (SclkS0 , SclkS1); --SclkS0:初始化 SclkS1建立17个脉冲
signal SclkSt : SclkState := SclkS0; --设置当前状态为SclkS0
--AD工作状态
type AdState is (AdS0 , AdS1 , AdS2 , AdS3 , AdS4 , AdS5 , AdS6 , AdS7 , AdS8); --AdS0:启动转换 S1:等待转换 S2:接收数据 S3:锁存数据
signal AdSt : AdState := AdS0; --设置当前状态为AdS0
signal SclkTmp : std_logic := '0'; --串行时钟临时信号
signal CsTmp : std_logic := '1'; --片选临时信号
signal Ad12 : std_logic_vector (11 downto 0); --Ad转换值
begin
--SclkTmp 状态机 建立读串行数据时钟18个方波脉冲
process (Clk)
variable Cnt : std_logic_vector (9 downto 0) := (others => '0'); --读数据时钟半波计数器
variable SclkCnt : std_logic_vector (4 downto 0) := "10010"; --读数据时钟数量计数器
constant SclkPw : std_logic_vector (9 downto 0) := "1111101000"; --串行时钟半周期计数值(必须>=2);计1000个Clk时钟、10us,频率50khz
begin
if (Clk 'event and Clk = '1') then
case SclkSt is
when SclkS0 =>
Cnt := (others => '0'); --计数器清零
SclkCnt := "10010"; --数量计数器初始值为18
SclkTmp <= '0'; --串行时钟变低
CsTmp <= '0'; --片选拉低
SclkSt <= SclkS1;
when SclkS1 => --产生18个串行时钟方波
if (Cnt < SclkPw - 1) then --小于半波宽度
Cnt := Cnt + 1;
else
Cnt := (others => '0'); --产生前17个串行时钟
if (Sclkcnt > 2) then --前16个时钟
SclkTmp <= not (SclkTmp);
if (SclkTmp = '1')then
SclkCnt := SclkCnt - 1;
end if;
elsif (Sclkcnt = 2) then --第17个时钟
SclkTmp <= not (SclkTmp);
if (SclkTmp = '1')then
SclkCnt := SclkCnt - 1;
CsTmp <= '1'; --片选拉高
end if;
else --第18个串行时钟,维持CS高电平
if (SclkTmp = '1')then
SclkSt <= SclkS0;
end if;
SclkTmp <= not (SclkTmp);
end if;
end if;
end case;
end if;
end process;
AdSclk <= SclkTmp; --将串行时钟送到AdSclk引脚
AdCs <= CsTmp;接下来写一段程序,按照时钟的上升沿、下降沿,去配置DIN、读取DOUT即可。
--AD 状态机
process (Clk)
variable Sts : std_logic_vector (1 downto 0);
variable Cnt : std_logic_vector (4 downto 0);
variable AdData : std_logic_vector (11 downto 0); --AD串行数据
constant RcW : std_logic_vector (1 downto 0) := "11"; --启动转换Rc低电平宽度。占3个时钟、60ns
begin
if (Clk 'event and Clk = '1') then
case AdSt is
when AdS0 => --开始
Sts := "00";
Cnt := (others => '0');
AdSt <= AdS1;
when AdS1 => --等待CS下降沿
Sts := Sts (0) & CsTmp;
if (Sts = "10") then
--Cnt := (others => '0');
AdDi <= '1'; --启动转换 START
AdSt <= AdS2; --下个CLK
end if;
when AdS2 =>
Sts := Sts (0) & SclkTmp;
if (Sts = "10") then
AdDi <= '1'; --选择通道0 SGL
AdSt <= AdS3; --下个CLK
end if;
when AdS3 =>
Sts := Sts (0) & SclkTmp;
if (Sts = "10") then
AdDi <= '0'; --选择通道0 ODD
AdSt <= AdS4; --下个CLK
end if;
when AdS4 =>
Sts := Sts (0) & SclkTmp;
if (Sts = "10") then
AdDi <= '1'; --高位在前 MSB
AdSt <= AdS5; --下个CLK
end if;
when AdS5 =>
Sts := Sts (0) & SclkTmp;
if (Sts = "10") then
AdDi <= '1'; --空位
AdSt <= AdS6; --下个CLK
end if;
when AdS6 =>
Sts := Sts (0) & SclkTmp;
if (Sts = "10") then
AdSt <= AdS7; --下个CLK
end if;
when AdS7 => --接收数据(串行时钟上升沿收取)
Sts := Sts (0) & SclkTmp;
if (Sts = "01") then
AdData := AdData (10 downto 0)& AdDo;
if (Cnt < "1011") then
Cnt := Cnt + 1;
else
AdSt <= AdS8;
end if;
end if;
when AdS8 => --锁存数据
Ad12 <= AdData;
AdSt <= AdS0;
end case;
end if;
end process;
AdQ <= Ad12;外部时钟频率100MHZ,内部降频到了50KHZ,代码已验证。可以直接拿去用,也可以在此基础上做一定的修改。
打完收工!